Macroevolution
Macroevolution: Large scale changes in the appearance of species are referred to as macroevolution. Usually these changes occur more slowly, over many generations. Evidence of macroevolution comes from a variety of fields of study:

Biogeography: Geographic variation in the beaks of Darwin's Finches in the Galapagos Islands.
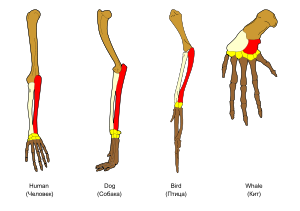
Comparative anatomy: Homologous bones of the forelimb in human, dog, bird, and whale.
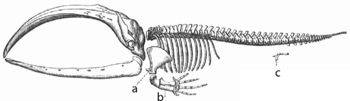
Vestigial Structures: Vestigial hindlimbs (c) of the baleen whale.
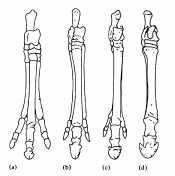
The Fossil Record: Changes over time in the leg and foot bones of horse ancestors.

Artificial Selection: Selective breeding has resulted in a wide variety of distinct dog breeds.

Comparing DNA sequences shows us the degree of relatedness between species.
- Biogeography: differences in a species over geographic space. example: Darwin's finches in the Galapagos Islands
- The Fossil Record: differences in a species over time. example: the changes in the skeletal structure of the horse lineage.
- Comparative Anatomy
-
- Homologous structures: structures that may have diverged due to different selective pressures, but which continue to share similarities due to common ancestry. example: bones of the arm and hand in a human, a bird, a bat, and a whale.
- Analogous structures: structures which have converged in multiple lineages to perform a similar function, but which are dissimilar in origin. example: the wings of insects and birds, the tails of fish and marine mammals.
- Vestigial structures: remnants of structures that used to serve a purpose, but which no longer do so, thus giving clues to an organism's ancestry. example: the vestigial hind limbs of whales, the non-functional eyes of cave dwelling fish, the pectoral and pelvic vestiges in snakes.
- Artificial Selection: directional selection imposed on a species by humans, for a desired (non-natural) outcome. example: selection on dogs to create breeds as distinct as the chihuahua and the great dane, selection on farm animals for greater yields of milk, meat, fur, eggs, etc. A great example from agriculture is the range of varieties created from Brassica oleracea, the wild mustard plant, including cabbage, kale, kohlrabi, brussels sprouts, cauliflower, and broccoli.
- DNA Comparison: comparison of DNA sequences of species to determine relatedness. example: DNA comparisons of human, chimpanzee, and orangutan.