Photosynthesis is one of the most important anabolic chemical reactions that allows life to exist on Earth. With water, light energy from the sun, and carbon dioxide from the air, photosynthetic organisms are able to build simple sugars. Organisms that can make their own food are called autotrophs, and are at the base of the food chain. The basic reaction is:
6 CO2 + 12 H2O + e --> 2 C6H12O6 + 6 O2
carbon dioxide + water + light energy --> glucose + oxygen
Oxygen molecules are colored to show their fate. Oxygen from CO2 ends up in glucose. Oxygen from water becomes free O2
Photosynthesis has two stages. Stage 1 requires light. Stage 2 can work in the light or in the dark. The energy accumulated in Stage 1 is used to drive Stage 2.
Experiment: We will conduct a simple experiment using spinach leaves to demonstrate that, in the presence of light and carbon dioxide, leaf tissues produce gas bubbles. While we cannot prove in this experiment that the bubbles are oxygen without a gas probe, we can demonstrate, by use of a control, that the bubbles only form when the leaves are submerged in a sodium bicarbonate solution (which releases CO2) and not when they are submerged in pure water. We can also demonstrate that the bubbles only form in the presence of strong light, by moving the experiment into the dark and making further observations. Finally, we could experimentally vary the light intensity to demonstrate the effect of light intensity on the process.
When we dissolve baking soda (NaHCO3) in water, carbonic acid (H2CO3) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH) are formed. The carbonic acid then breaks down into water and carbon dioxide gas, which is why dissolving baking soda in water causes it to fizz.
NaHCO3 + H2O --> H2CO3 + NaOH
H2CO3 --> H2O + CO2 (gas)
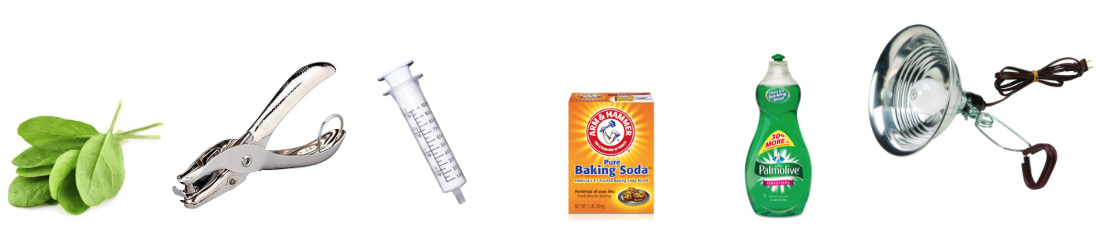
Materials:

Methods:
Watch this demonstration to see how to make the leaf disks sink.
Results:
In the light, you should expect to see the disks in the control solution (water) stay on the bottom, but the disks in the treatment solution (baking soda) should begin to rise as they use the CO2 to undergo photosynthesis and produce oxygen bubbles. The bubbles should cause the disks to float. After you remove the light and place the cups in the dark, the treatment disks should stop undergoing photosynthesis and the disks should begin to sink.
For comparison purposes, each lab group that does this procedure should report the time at which half (5) of the disks is floating. In the example below, that time would be about 11.5 minutes. You can use this Excel spreadsheet to record your data and it will auto-generate a graph for you.
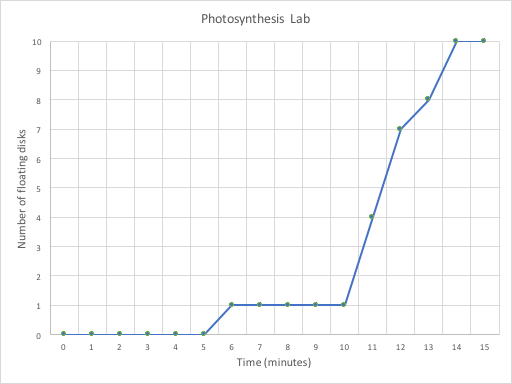
Some or all of the submerged disks should begin to float within about 15 minutes
Questions:
References:
http://media.collegeboard.com/digitalServices/pdf/ap/bio-manual/Bio_Lab5-Photosynthesis.pdf
http://www.biologyjunction.com/5b-photoinleafdiskslesson.pdf
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XV9FOWleErA
http://www.berwicksclasses.org/AP%20Biology/Biology%20Assignments/AP%20BIOLOGY%20Lab%204.htm
http://www.kabt.org/2008/09/29/video-on-sinking-disks-for-the-floating-leaf-disk-lab/