LECTURE 5. CHAPTER 6 - Microbial Growth
Physical requirements for the growth of microorganismsWHAT FACTORS AFFECT GROWTH?
- Physical factors - temp, pH, water, oxygen, pressure
- Nutrients - Cell constituents and energy sources
1. Temperature:
How does temperature affect optimal growth?
- minimum, optimum, maximum temperatures for growth
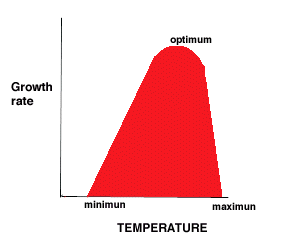
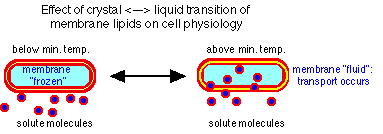
- Minimum - no growth below this temperature
- enzymes don't function
- transport ceases
- cells dormant not dead
- dangers of freezing and thawing
- Optimum - closer to maximum than minimum (5 to 10 C below max)
- Maximum - Bacterium A grows at temperatures up to 40°C. What might be happening to the cell at 41°C?
- Categories based on optimum temperatures:
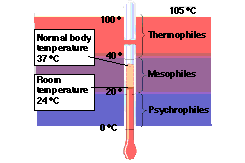
- psychrophiles <20 C
- high levels of unsaturated fatty acids --> remain fluid at low temperature
- mesophile 20-40 C
- thermophile >40 C and < 65 C
- extreme thermophiles > 65 C
- hot water heaters, hot springs, vents
- E.g. Pyrodictum, min 82 opt 105 max 110 C
- extremes have lipids, proteins adaptation
- PCR - Thermus aquaticus
- require hydrogen ions for membrane integrity
- do not survive at neutrality
- prevent uptake into cytoplasm and pump out
- pump in protons
- generate ammonia (+) by ammino acid degradation
| Bacteria | min pH | opt pH | max pH | |
| Thiobacillus | 1.0 | 2-2.8 | 4-6 | |
| E. coli | 4.4 | 6-7 | 9.0 | |
| C. sporogenes | 5.4 | 6-7.6 | 9.0 | |
| P. aeruginosa | 5.6 | 6.6-7 | 8.0 | |
| Nitrobacter | 6.6 | 6.6-8.6 | 10.0 | |

3. Classification based on water activity/osmotic pressure (remember, low water activity = high osmotic pressure)
- halophiles- require sodium >9%; extremes may live in 30%
- marine salt about 3%
- cell wall and membrane fall apart w/o sodium
- nonhalophile - 0 to 1.5%
How do microbes adapt to low water activity?
- Microbes can change their internal osmotic environment
- E. coli in GI tract
- produce or import compounds that increase internal solutes
- compatible solutes - do not harm host
- ions, sugars, amino acids
4. Oxygen:
How does oxygen affect optimal growth?
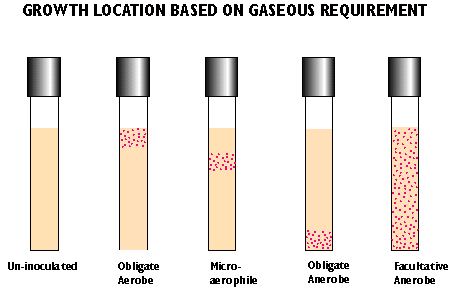
- aerobes - require oxygen
- obligate/strict anaerobes - killed by oxygen
- aerotolerant anaerobes - does not require oxygen but not killed
- facultative anaerobe - grows in presence or absence of oxygen with different metabolic strategies
- microaerophiles - require reduced levels of oxygen
Why is oxygen toxic to some microbes?
- metabolic byproducts all organisms produce are toxic to cells
- hydrogen peroxide
- superoxide
- present in WBC to kill bacteria
- aerobes have catalase and/or peroxidase and superoxide dismutase (SOD)
- catalase: 2H202 -> 2H20 + 02
- peroxidase: H202 + 2H+ -> 2H20
- SOD: 202- + 2H+ -> 02 + H202
- strict anaerobes lack these enzymes
- microaerophiles either reduced amounts of these enzymes or oxygen-sensitive forms of enzymes
- aerotolerant have these enzymes but not those used in aerobic metabolism
- Toxic forms of oxygen are broken down by several enzymes; one of these is catalase. This enzyme breaks down hydrogen peroxide to form water and molecular oxygen. Our tissues as well as many microorganisms are catalase positive - thats why the bubbles when you pour peroxide on a cut.
Why would our tissues have peroxide in them?
Some theories of cancer hypothesize that oxidants (like toxic forms of oxygen) damage DNA and thus cause the mutations which in turn cause cancer. These theories predict that antioxidants such as beta-carotene, vitamin E and vitamin C would thus have anti-mutation activity.
commonly called vitamins, these are organic substances required for the growth of an organism but which the organism can not synthesize.
What is the difference between a defined and an undefined medium?
WHAT FACTORS AFFECT GROWTH?
- Nutrients - Cell constituents and energy sources
- Physical factors - temp, pH, water, oxygen, pressure
I. Nutrients:
| ELEMENT | CELL FUNCTION | ||||||
| C | backbone of organic cell components, energy | ||||||
| H | water, organic components, pH, hydrogen bonds, re-dox | ||||||
| O | water, organic components, respiration | ||||||
| N | amino acids, nucleotides, coenzymes, ATP | ||||||
| S | amino acids, coenzymes, enzymes | ||||||
| P | nucleic acids, phospholipids, coenzymes, ATP | ||||||
| Fe | cytochromes, enzymes | ||||||
| Na, K, Ca, Cl, Mg, Mn | Trace elements: transport, ionic balance, cofactors (e- donor/acceptors) | ||||||
II. CLASSIFICATION OF ORGANISMS BASED ON carbon, energy, and electron sources
- Chemotrophs - Derives energy from chemicals
- Phototrophs - Derives energy from sunlight
- Autotrophs - Use carbon dioxide for carbon
- Heterotrophs - Use organic substrates for carbon
- Lithotrophs - Inorganic compounds for electrons
Bacterial Growth
- Bacteria grow by binary fission. Starting with one organism how many organisms would you have after 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12 generations.
- Increase in cell numbers
- Binary fission
- Budding
- Fragmentation
- DNA duplication
- DNA repication
- single origin of replication, bidirectional
- theta intermediate
- Separation of DNA and cytoplasmic contents
- Cross wall formation
- time required for a cell to divide or a population to double
- 1 to 2 or 100 to 200 or 1 million to 2 million
- Most common bacteria have a generation time 30-60 min under opt. conditions.
- Most common pathogens in the body, about 5-10 hours.
- Why doesn't it grow immediately?
- What determines how fast it grows?
- Why does it stop growing?
- Lag phase - synthesis of new components or repair
- Log phase - reproduction at maximum rate (shortest generation time)
- exponential growth 1->2->4->8->16->32->64
- Stationary phase - no net increase, balance between cell division, cell "death", maintenance
- Death phase - do they really die?
If you started with 10 organisms, how many would you have after each of the above generations?
What is microbial growth?
| Mycobacterium tuberculosis (in lab) | 12 hrs |
| Clostridium botulinum (in lab) | 0.58 |
| E. coli (in lab) | 0.30 |
| E. coli (in mouse) | 20 hrs |
What happens when you inoculate a single bacterium from slant stored in refrigerator into nutritional medium and incubate?
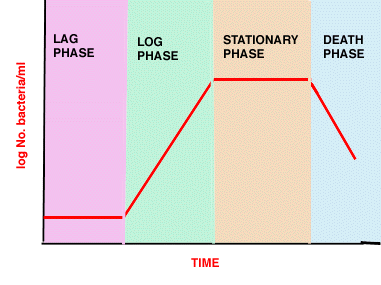
Phases in bacterial growth in batch culture
(see above picture)
GROWTH EQUATION: Log Bf = LogBi + .3t/dt
PRACTICE PROBLEM: A culture is inoculated at noon with 103 cells/ml. At 10 pm the population is determined to be 109 cells/ml. What is the doubling time? Describe the phases of bacterial growth.
PRACTICE PROBLEM: A culture is inoculated at noon with 103 cells/ml. At 10 pm the population is determined to be 109 cells/ml. What is the number of generations? What is the doubling time?
Write out the growth equation
n = Log10 f - Log10 i/0.3
Indicate the known and unknown values
Log10 f = 9, Log10i = 3, t = 10, n = ?
Substitute the values and do the math
n = 9 - 3 = 6/0.3 = 20 generations
Generation time equation = (g = t/n)
Substitute values: g = 10 hr/20 = 0.5 hr = 30 min/doubling