Igneous Rocks
-
Igneous rocks (Granites).
Igneous rocks are formed by the crystallisation of a magma. The difference
between granites and basalts is in silica content and their rates of cooling.
A basalt is about 53% SiO2, whereas granite is 73%.
-
Intrusive, slowly cooled
inside the crust. (Plutonic rock = formed in the earth). Large crystals.
-
Granite. (Continental
crust) Density 2.7-2.8. High silica content (acidic). = quartz + mica +
K-feldspar in solid solution. 60% orthoclase and plagioclase fledspars
+ 25% quartz + 5% darker minerals (biotite, hornblende). Color from flesh
to black. Crystals intermingled. Hard, rigid, tough. Granitic rock is much
less common on the other terrestrial planets, a fact having to do with
the fractionation (where early crystallizing minerals separate fromt he
rest of a magma), a process that takes place uniquely on earth, due to
the prevalence of plate tectonics.
-
Granodiorite. An intermediate
form between granite and diorite.
-
Diorite. High silica
content (acidic)
-
Gabbro. Density? Medium
silica content. (intermediate). Similar to granite = quartz + feldspar
+ pyroxene + amphibole + mica + olivene. A layer of gabbro is found in
the ocean crust, unerneath the basalt layer (0.5-2.5km), from 2.5 to 6.3
km deep. The lunar highlands have many gabbros (made largely of potassium
feldspar - also known as plagioclase)
-
Peridotite.
-
Extrusive. cooled rapidly
at the surface. Small crystals.
-
Rhyolite. Medium silica
content (intermediate). A fine-grained volcanic rock of granitic composition.
-
Dacite.
-
Andesite. (Volcanic arcs)
Density >2.8. Low silica content (basic) = sodium feldspar + amphibole.
Dark, dense.
-
Basalt. (Ocean crust)
Density 2.9. Low silica content. (basic). Dark, dense. = olivene + pyroxene
+ Ca-Feldspar in solid solution. Basaltic rocks (gabbro & basalt) are
made up of feldspars and other minerals common in planetary crusts. They
have been identified as major surface rocks on the dark lunar planes and
much of Mars, Venus and the asteroid Vesta.
-
Pyroclastic
rocks: debris ejected by volcanoes
-
Tuff is made of compacted
debris from old volcanic ash showers.
-
Volcanic breccia is composed
of angular mineral fragments embedded in a matrix, the product of explosive
eruptions.
-
Ignimbrites are sheets
of coalesced fine particles which once flowed at high speed, extremely
hot, fluid avalanches.
Notes: Density in kg/litre or
g/cm3
|
Classification
of igneous rocks
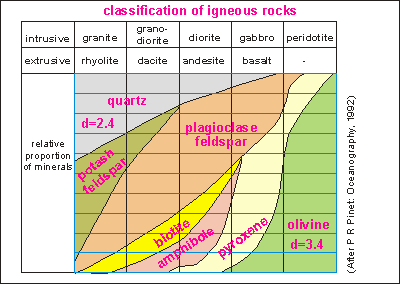 This
diagram shows the makeup of igneous rocks from the various minerals inside
a magma chamber. Density increases from bottom right to top left. This
diagram shows the makeup of igneous rocks from the various minerals inside
a magma chamber. Density increases from bottom right to top left.
Intrusive rocks are coarse-grained
in texture and crystallise slowly from magma deep in the earth's crust.
Extrusive rocks are fine-grained in texture and crystallise quickly from
lava on or near the earth's surface. The mineralogy determines the type
of rock. Granites and rhyolites consist predominantly of quartz and potash
feldspar; gabbros and basalts, predominantly of pyroxene and plagioclase
feldspar. Other rock types have intermediate mineral compositions. Note
that amphibole = horneblende. Note that the density of the minerals increases
from top left (2.6) to bottom right (3.4). Top left: high silica content
(acidic); bottom right: low silica content (ultrabasic). The temperature
range at which magma solidifies is 1100-700ºC.
(Paul R Pinet in Oceanography,
an introduction to Planet Oceanus. 1992.) |
| |