Introduction: Organisms and nature are systems in the sense that they are comprised of components that interact with each other. An organism, like the human body, is delimited and has obvious boundaries with internal controls. An ecosystem has boundaries and controls, too, but they are not as easy to perceive since it is not demarcated by an obvious boundary. Feedback is an important part of the function of these systems.
Feedback: Feedback occurs when a system produces an output, e.g., body heat, and part of that output is used to affect future output, e.g., the continued production of body heat. In the diagram of the feedback loop on the right, part of the output from A is routed back as B to become part of the input that is used to produce future output. When B is negative, there is negative feedback which causes the system to decelerate and move toward an equilibrium. When B is positive, there is positive feedback which causes the system to accelerate and move  toward a new system state. Positive feedback makes a system unstable. toward a new system state. Positive feedback makes a system unstable.
Organism: There are many chemical reactions on which an organism depends: those that replace wornout cells, muscular contractions, thinking, etc. These reactions would be slow at body temperature but cellular enzymes speed them up in the temperature range of the body. Without enzymes, the reactions would go much faster when the temperature is higher, but those higher temperatures would destroy the proteins in a living body. Maintaining a cellular environment, specifically temperature, that facilitates essential chemical pathways required for survival is a very important reason to maintain homeostasis.
The normal temperature of a human body is said to be 37°C. Cells in the hypothalamus detect the temperature of the blood. When the blood temperature moves away from normal, the hypothalamus sends signals to other parts of the body that result in responses that return the temperature back to normal.
 Click image
Click image
|
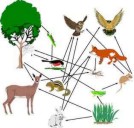
Ecosystem: Ecological systems may vary in their component species, but all have some common characteristics. Energy enters the ecosystem from the outside, often from the sun but may be as detritus or chemical energy. It flows through the species as they obtain their own energy, and the energy they use exits as heat. Nutrients cycle and recycle among the organisms in the ecosystem and between organisms and inorganic forms. The species comprising an ecosystem tend to change with time (there is a succession) as more organic matter accumulates and the organisms themselves moderate the variations in abiotic factors: temperature, light, moisture, etc. Diversity of species, of habitat, of structure increase. In mature ecosystems, the organisms constitute a reservoir of biomass (energy in organic form) and nutrients. Moreover, the environment within the ecosystem tends to be less variable than outside of it. The successional process is inherently unstable. However, the final climax stage of succession tends to be diverse and stable.
 Click image
Click image
|
Although more loosely connected than the organs and tissues of an organism, the components of the ecosystem interact through the food web, by which energy flows and nutrients cycle. Feedbacks operate through organism interactions as herbivores increase or decrease their populations in response to changes in plant production, and predators respond to changes in herbivore populations. Stability and balance in the ecosystem depend on the feedbacks generated by the diversity of species.
Events, like fires, floods, storms, can alter or delay progression of the ecosystem toward maturity, but it usually recovers (through negative feedback) and continues to mature (through positive feedback).
Summary: Feedbacks are common in natural systems. Positive feedbacks are operative as individuals and ecosystems grow to maturity, changing state but ultimately reaching greater stability. They are also operative as state changes toward a less stable situation, e.g., eliminating more forests with increasing demand for timber, draining more wetlands and coastline as demand for second and vacation homes increases, drilling for oil in ever more sensitive ecosystems as the economy requires a growing supply of fossil fuel, and in the exploding and less stable human population. Negative feedbacks are an essential part of a stable system, unless they are overwhelmed by shocks to the system or by relatively short-term economic and political objectives. A way to measure how special an organism is may be by its contribution to stability or instability.
|


